You didn’t know that these 10 all-electric vehicles existed in the 90s.
Published new article on Medium: https://kusmat.medium.com/you-didnt-know-that-these-10-all-electric-vehicles-existed-in-the-90s-3c7d2cde2826?source=friends_link&sk=bb7e276851d814c2bf130f8325dc9f1c
You didn’t know that these 10 all-electric vehicles existed in the 90s.
Python and Pandas data analysis of electric vehicles market in the USA.

Jupyter notebook: https://github.com/kusmat/Electric_vehicles_USA_Extinct/blob/9f1628aed01396d446a2993ce990c07f1ba918f1/Extinct%20Electric%20Vehicles%20USA.ipynb
Introduction
Electric vehicles are becoming more and more popular today as Tesla is the precursor to the increase in the manufacturing of electric vehicles, but have you ever wondered what was the first all-electric vehicle ever manufactured in the USA?
Was it TESLA or was it something else?
Below I go in details into this analysis of USA car manufacturing for electric vehicles.
USA Electric vehicles
Looking at the evolution of the electric vehicle manufacturing over the years and their popularity at the moment, you might wonder what companies produce electric vehicles and how many different electric vehicles are there in the USA now.
Trend below shows number of electric vehicle models being manufactured in the USA since 1998.
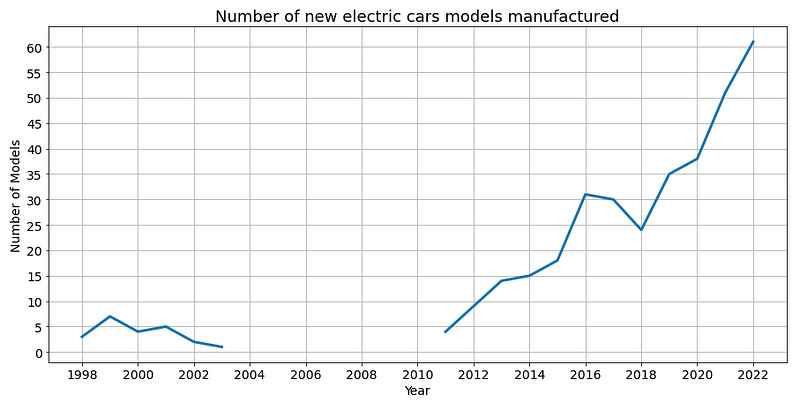
But how many car manufactures have decided to adopt electric cars?
Trend below shows number of electric car manufacturers in the USA. We can see that the number of models is increasing but number of manufacturers or makes stays pretty much constant.
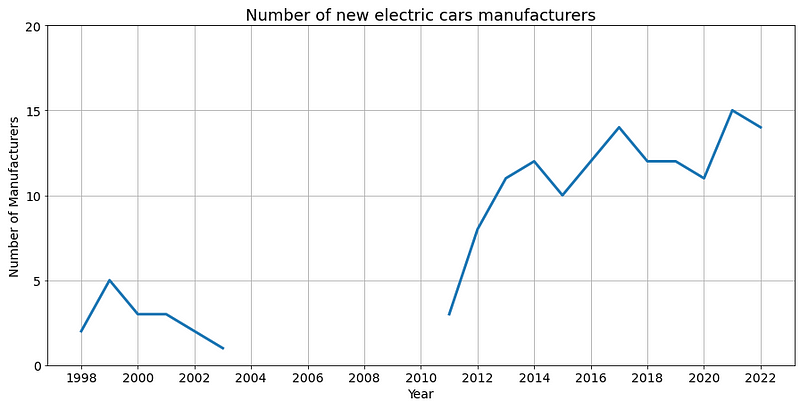
Interesting fact that there was an attempt to start manufacturing electric cars in the 90’s, particularly with Chevrolet and Honda in 1998! Unfortunately all of them were discontinued by year 2003.
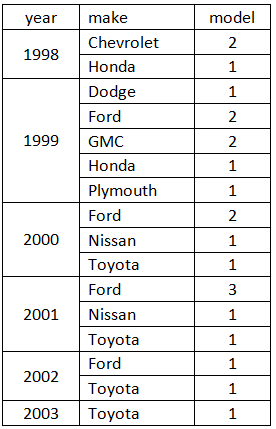
Table below summarizes number of model manufactured each year.
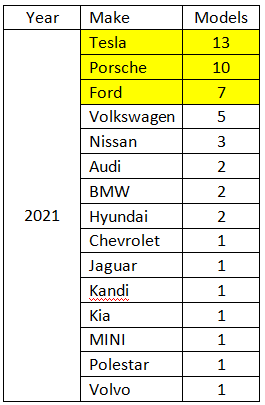
Currently the main manufacturers of the electric vehicles are Tesla, Porsche and Ford, with others still dragging behind them.
We are going to explore infamous electric vehicles from the past that unfortunately did not do so well and have become extinct.
Table below list all the models and when they started the life.
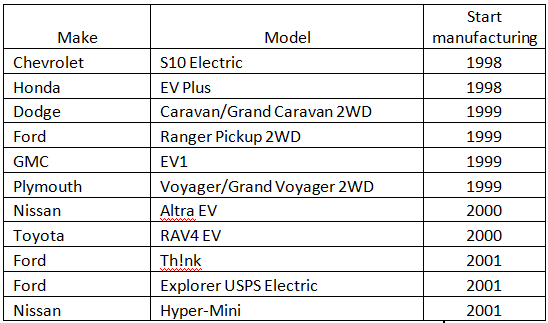
We will take a closer look at each model.
1. Chevrolet S10 Electric
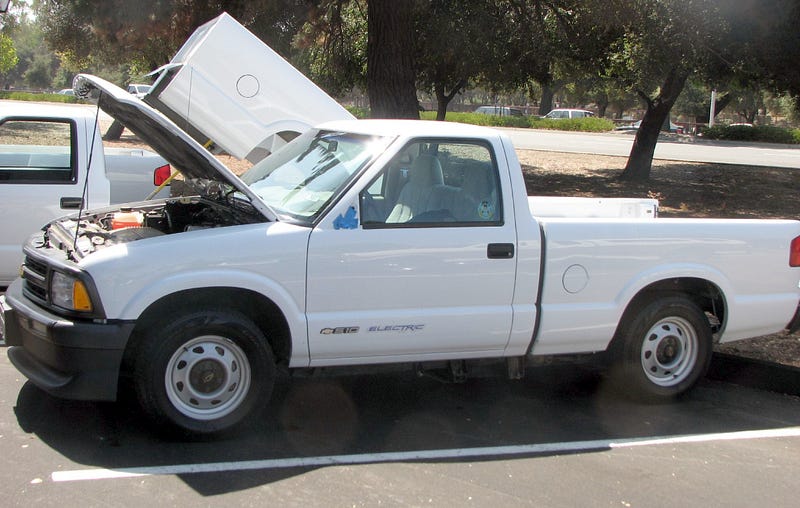

The Chevrolet S-10 Electric was an American electric-powered vehicle built by Chevrolet. It was introduced in 1997, updated in 1998, and then discontinued. It was an OEM BEV variant of Chevrolet’s S-10 pickup truck. The S-10 Electric was solely powered by electricity, and was marketed primarily to utility fleet customers.
More information on Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chevrolet_S-10_EV
2. Honda EV Plus
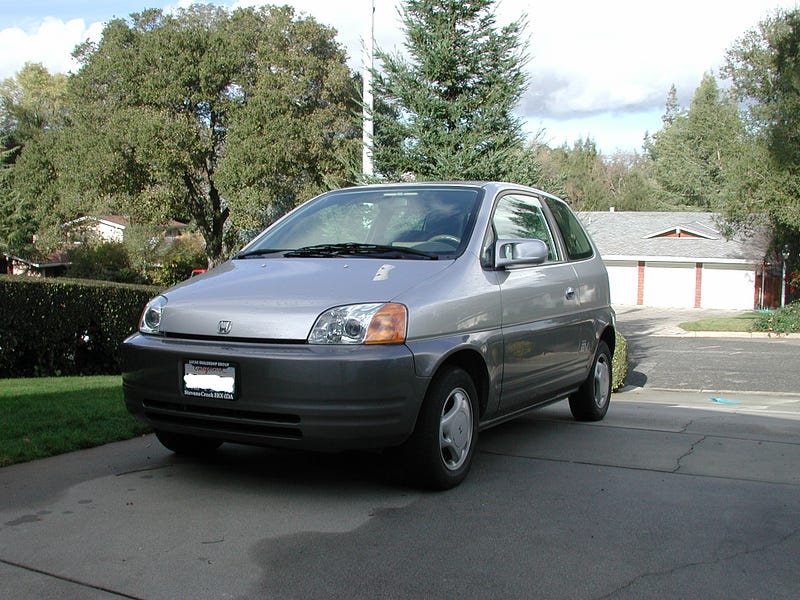

The Honda EV Plus was the first battery electric vehicle from a major automaker that did not use lead acid batteries. Roughly 340 EV Plus models were produced and released. Production of the EV Plus was discontinued in 1999 after Honda announced the release of its first hybrid electric vehicle, the Honda Insight.
The EV Plus served to test advanced battery chemistry in an electric car and also met California Air Resources Board requirements for zero-emission vehicles, like the General Motors EV1. It also tested the pancake-style motor, electronic control unit, power control unit and the Nickel–metal hydride battery (NiMH) later used in Honda hybrids and developed further in the first Honda FCX Fuel Cell Vehicles, which were rebuilt from returned (decommissioned) EV Plus chassis.
More on Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Honda_EV_Plus
3. Dodge Caravan EPIC
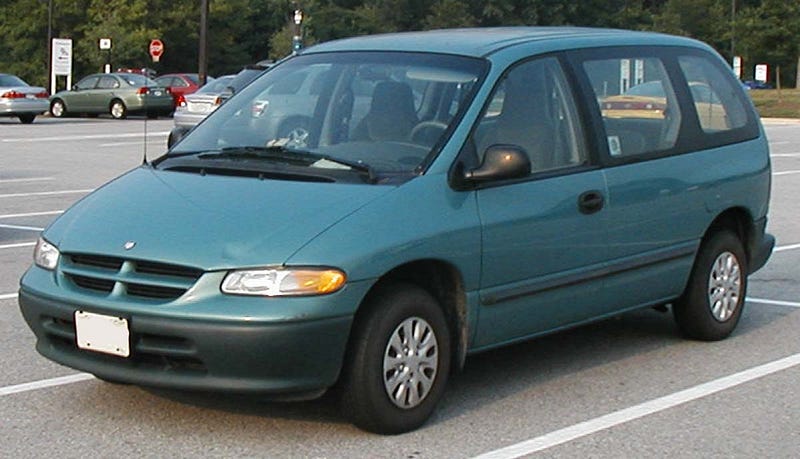

In 1999, Dodge introduced the Caravan EPIC, a fully electric minivan. The EPIC was powered by 28 12-volt NiMH batteries and was capable of traveling up to 80 miles (130 km) on a single charge. The EPIC was sold as a fleet-only lease vehicle. Production of the EPIC was discontinued in 2001. Only a few hundred of these vehicles were produced and sold. After the leases expired they were returned and crushed. Approximately 10 vans remain in private hands today.
More information available:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dodge_EPIC and https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dodge_Caravan
4. Ford Ranger EV
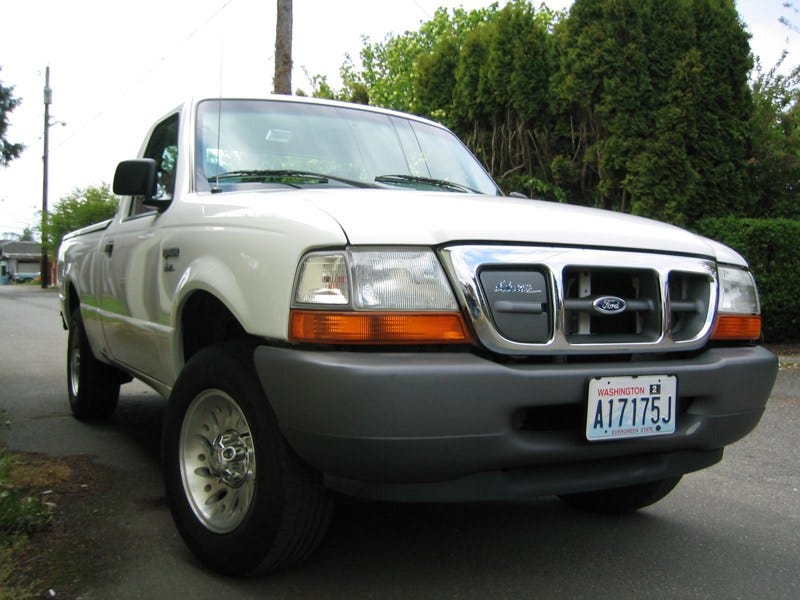

The Ford Ranger EV (Electric Vehicle) is a battery powered compact pickup truck that was produced by the Ford motor company. It was produced starting in the 1998 model year through 2002 and is no longer in production. It is built upon a light truck chassis used in the Ford Ranger. A few vehicles with lead-acid batteries were sold, but most units were leased for fleet use. A few persistent and interested private parties were able to obtain leases over a period of three to five years.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ford_Ranger_EV
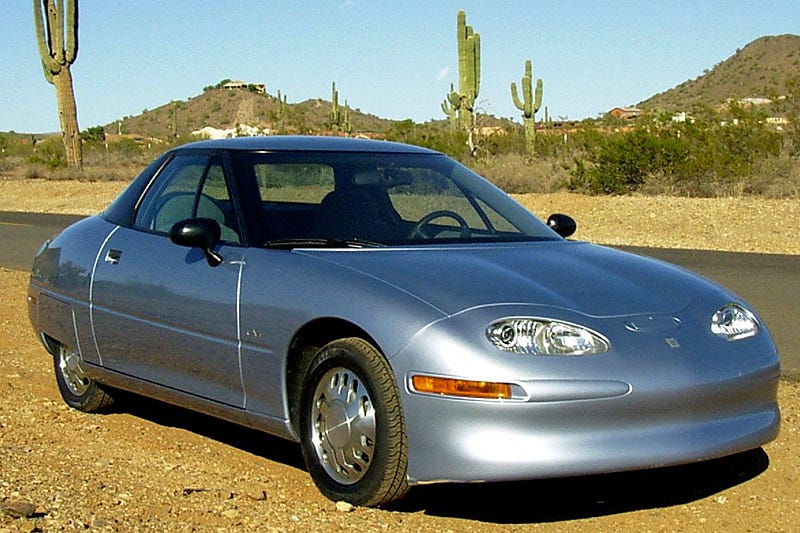
5. GMC EV1

The General Motors EV1 was an electric car produced and leased by General Motors from 1996 to 1999. It was the first mass-produced and purpose-designed electric vehicle of the modern era from a major automaker and the first GM car designed to be an electric vehicle from the outset.
The decision to mass-produce an electric car came after GM received a favorable reception for its 1990 Impact electric concept car, upon which the design of the EV1 drew heavily.
More information on: General Motors EV1 — Wikipedia
6. Nissan Altra EV

The Nissan Altra was an electric car produced by Nissan Motors between 1998 and 2002. The Nissan Altra was introduced at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. Nissan described the Altra as a combination of a sedan, SUV, and minivan. It was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as electric utilities. Only about 200 vehicles were ever produced. It used the bodystyle of the Nissan R’nessa.
According to Nissan, the Altra had a maximum range of 120 miles (190 km). The Environmental Protection Agency reported that the 2000 version had an adjusted mileage (miles per equivalent of a gasoline gallon) of 117 mpg‑US (2.01 L/100 km; 141 mpg‑imp) the city, and 130 mpg‑US (1.8 L/100 km; 160 mpg‑imp) on the highway.
More information: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nissan_Altra
7. Toyota RAV 4 EV
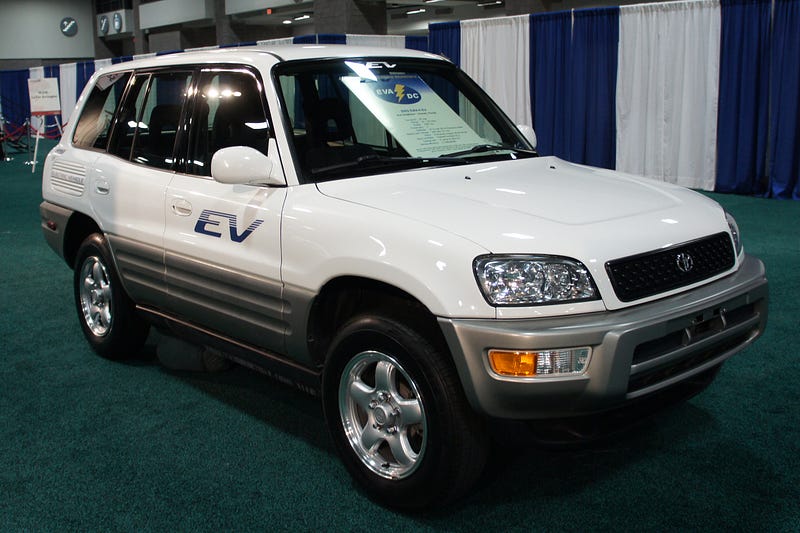

The Toyota RAV4 EV is an all-electric version of the popular RAV4 SUV produced by Toyota until 2014. Two generations of the EV model were sold in California, and to fleets elsewhere in the US, with a gap of almost ten years between them.
The first generation was leased from 1997 to 2003, and at the lessees’ request, many units were sold after the vehicle was discontinued. A total of 1,484 were leased and/or sold in California to meet the state’s mandate for zero-emissions vehicle. A small number were sold or leased in fleet sales in other states. As of mid-2012, there were almost 500 vehicles still in use in California.
The first fleet version of the RAV4 EV became available on a limited basis in 1997. In 2001 it was possible for businesses, cities or utilities to lease one or two of these cars. Toyota then actually sold or leased 328 RAV4 EVs to the general public in 2003, at which time the program was terminated despite waiting lists of prospective customers.
The RAV4 EV closely resembles the regular internal combustion engine (ICE) version — without a tailpipe — and has a governed top speed of 78 mph (~126 km/h) with an EPA rated range of 95 mi (153 km). The 95 amp-hour NiMH battery pack has a capacity of 27 kWh, charges inductively and has proven to be very durable. Some RAV4 EVs have been driven more than 150,000 miles (240,000 km) using the original battery pack. It was also one of the few vehicles with a single speed gearbox when introduced to the market.
More information: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toyota_RAV4_EV
8. Ford Th!NK
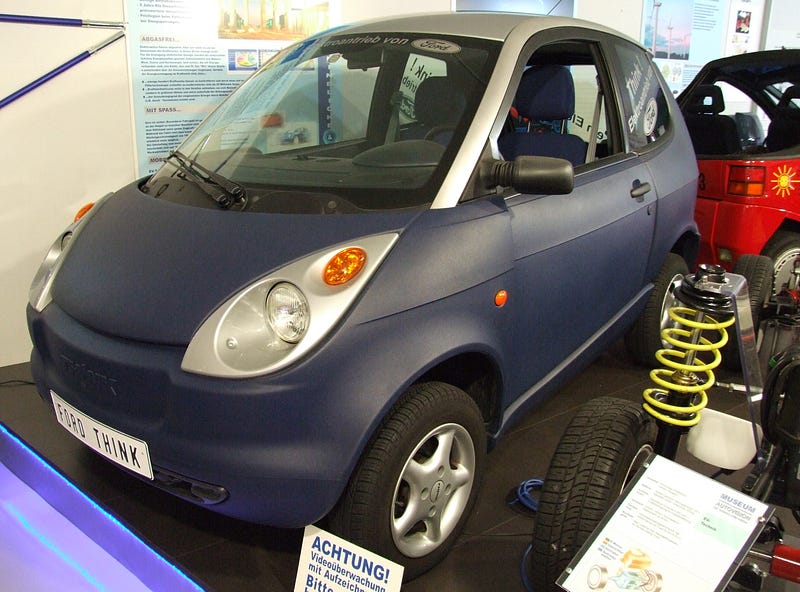

Ford TH!NK was a line of electric vehicles produced by the TH!NK Mobility, then an enterprise of Ford Motor Company. The short-lived line included four models: the TH!NK Neighbor and the TH!NK City, small electric automobiles, and the TH!NK Bike Traveler and the TH!NK Bike Fun, electric-powered motorized bicycle. Ford sold its stock, and the resulting company, Think Global, produced electric cars in Norway until declaring bankruptcy in 2011.
More information: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ford_TH!NK
9. Ford Explorer USPS EV
Not much information and pictures are available about this vehicle.
Some information can be found on this link: https://www.officialdata.org/cars/Ford/Explorer%20USPS%20Electric
10. Nissan Hyper Mini
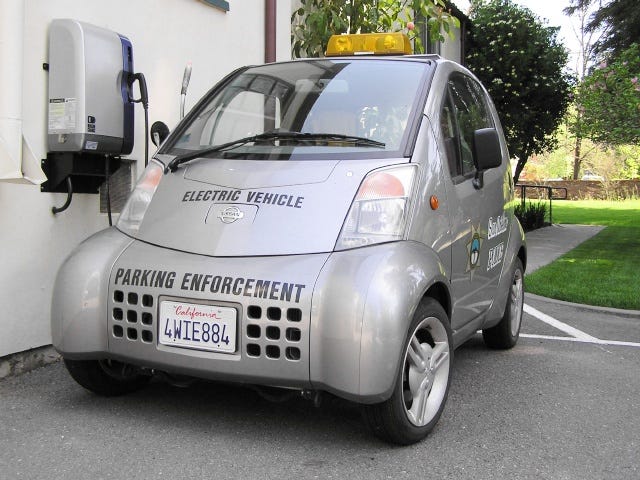

The Hypermini is a two-passenger EV (electric vehicle) microcar that can move at 100 km/h (62 mph) and travel about 115 kilometres (71 mi) on a single charge, according to Nissan’s measurements made under Japan’s 10–15 test mode.
It was introduced in a limited way in Japan in 1999. It was launched for retail sale through Nissan dealers in the greater Tokyo, Osaka, and Kyoto metropolitan areas in February 2000 with a 200-volt mount-type battery charger and with 200 volt non-fixed battery charger. Sales were targeted principally at national government offices and agencies, local government bodies and corporations. Nissan claims the Hypermini consumes a quarter the energy of a typical car.
According to Nissan, a total of about 300 were made. Production versions were trialed in the Japanese cities of Kyoto (138), Yokohama (20), Ebina (15), Tokyo (20), and in California at University of California, Davis (15) and the city council of Pasadena (11).
More information: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nissan_Hypermini
Summary
We can see that this is not the first time that electric vehicles are being manufactured. Hopefully now with the advancement in technology, the electric vehicle market with thrive.
Let me know your opinion about electrical cars market in the comments to this article. Thanks for reading!
To see more informative content like this, go to: www.kusmat.com.
Comments